P.P.S. Want to learn more about exponential technologies and home in on your MTP/ Moonshot? Abundance Digital, a Singularity University Program, includes 100+ hours of coursework and video archives for entrepreneurs like you. Keep up to date on exponential news and get feedback on your boldest ideas from an experienced, supportive community. Click here to learn more and sign up.
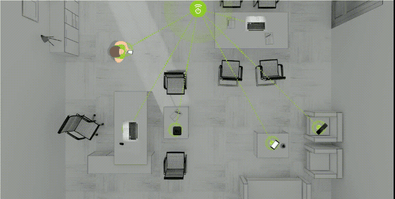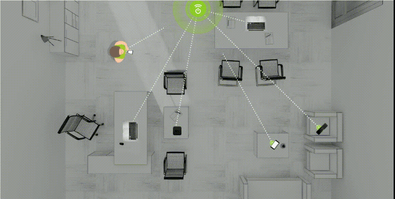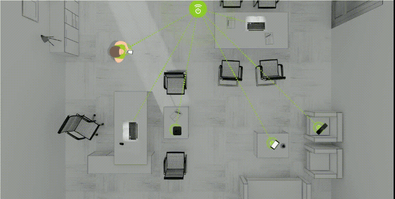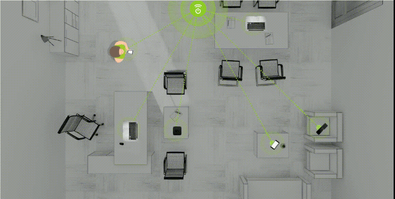 What it is: The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has now granted authorization for wireless power delivery to an Internet of Things (IoT) tracking device. In effect, Ossia’s “Cota” technology will soon be utilized in Walmart’s highly complex supply chain, embedded in shipping packages across a number of transit vessels. Having developed what’s known as “trickle charging” capacity, Ossia uses radio frequency (RF) to send power and data from Cota transmitters over distances greater than 15 feet. This technology allows for the charge of dozens of mobile devices within a several-meter radius, sometimes even through walls. Transmitters come in multiple form factors, including a drop ceiling tile, which would communicate with sensors embedded in shipping packages aboard trucks. The system might also be used in crowded spaces, such as coffee shops or offices, wherein two Cota ceiling tiles could be linked to power mobile devices.
What it is: The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has now granted authorization for wireless power delivery to an Internet of Things (IoT) tracking device. In effect, Ossia’s “Cota” technology will soon be utilized in Walmart’s highly complex supply chain, embedded in shipping packages across a number of transit vessels. Having developed what’s known as “trickle charging” capacity, Ossia uses radio frequency (RF) to send power and data from Cota transmitters over distances greater than 15 feet. This technology allows for the charge of dozens of mobile devices within a several-meter radius, sometimes even through walls. Transmitters come in multiple form factors, including a drop ceiling tile, which would communicate with sensors embedded in shipping packages aboard trucks. The system might also be used in crowded spaces, such as coffee shops or offices, wherein two Cota ceiling tiles could be linked to power mobile devices.
Why it’s important: We are currently witnessing an unprecedented explosion in IoT-connected sensors, embedded in our devices and environments. Stanford researchers estimate that connected devices will number over 500 billion by 2030. Yet the cost and technological constraints of keeping devices continually charged has proved a major barrier to mass adoption. Regulatory approval of newly sophisticated wireless charging technology will tremendously catalyze mass integration of continuously reliable tracking devices and IoT integration across almost every industry imaginable, transforming tomorrow’s supply chains. | Share on Facebook.
Source
Astronomers spot ‘cosmic web’ that sticks the universe together.
What it is: For the first time ever, astronomers have directly observed the cosmic web. Serving as a “glue” between far-afield galaxies, the cosmic web is essentially the universe’s underlying structure at its largest scale. While only using indirect evidence, today’s leading models indicate large filaments of gas and galaxies that crisscross the universe. These filaments form threads of superclusters and clusters, thus mimicking the web of a spider. Most recently, astronomers used the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope to peer back at an ancient galaxy cluster at a distance of over 12 billion light-years. From their images, the astronomers then used specialized equipment to map out light emitted by hydrogen within the SSA22 galaxy cluster, spotting individual gas filaments linking the galaxies together.
Why it’s important: This observation provides definitive support for our current models of the universe. As Durham University astrophysicist and co-author Michele Fumagalli states, “It is very exciting to clearly see for the first time multiple and extended filaments in the early universe [...] We finally have a way to map these structures directly and to understand [...] their role in regulating the formation of supermassive black holes and galaxies.” Offering explicit visual validation, this and similar discoveries will help us make tremendous strides in understanding the evolution of our early universe. | Share on Facebook.
Source
Astronauts just printed meat in space for the first time — and it could change the way we grow food on Earth.
What it is: Last month, astronauts on the International Space Station successfully proved that lab-grown beef can be produced even under extremely hostile conditions— in this case, microgravity. Using a magnetic printer developed by Russian firm 3D Bioprinting Solutions, the cosmonauts adapted a method designed by Israeli startup Aleph Farms to coax bovine cells into fully formed muscle tissue. After biopsy-extracted cow cells were immersed in a nutrient broth (which simulates the interior environment of a cow’s body), the bioprinter fostered their “growth” into a tiny piece of beef, even in the absence of sunlight and gravity.
Why it’s important: As cutting-edge startups like Memphis Meats and JUST continue to charge ahead with lab-grown meat in controlled Earthbound environments, developments such as space-based meat bioprinting has a two-fold impact on the food industry. Beyond its promise for food production aboard the ISS and in future space colonies, Aleph Farms and 3D Bioprinting Solutions’ success could dramatically advance alt-meat production here on Earth. As Aleph Farms CEO Didier Toubia put it, “We are proving that cultivated meat can be produced anytime, anywhere, in any condition.” Such a proof-of-concept could thereby lead to on-demand, high-protein meat production in some of Earth’s harshest environments, granting immediate access to nutrition even within remote populations. | Share on Facebook.
Source
Toyota Research Institute teaches mobile manipulator with VR, simulation.
What it is: Scientists from the Toyota Research Institute (TRI) are now training robots to navigate and assist with domestic tasks in people's homes. Using complex simulations and virtual reality (VR), Toyota has successfully designed and trained robots that can perform multi-step assignments, such as loading a dishwasher or transferring a bottle from fridge to table. By processing robots’ audiovisual sensor data, building physical world models, and mapping visual inputs to taught behaviors, TRI’s software architecture enables robots to navigate uneven terrain, circumvent unexpected obstacles, respond to voice commands, and autonomously execute chores. Furthermore, because learning is readily transferred between robots, the lessons learned by one bot can be applied to the entire fleet, allowing for rapid, iterative progress and training en masse.
Why it’s important: Building effective home assistants is a significant prong of Toyota's future strategy. Particularly in light of an aging population and the economic challenges that accompany this demographic trend, TRI hopes that its versatile and fast-advancing robotics initiative could help people “age in place.” Yet aside from allowing elderly individuals to stay in their homes—particularly those that cannot afford to rely on scarce human aid—TRI’s initiative is a critical stepping stone en route to countless residential and commercial robotic assistants. Whether in manufacturing, pick-and-place operations, logistics or packing, fleet learning and iterative training are about to revolutionize mass market adoption of robots that can learn almost any task, on the spot. | Share on Facebook.
Source
Microsoft wants to connect another 40 million global internet users.
What it is: In 2017, Microsoft launched its “Airband Initiative” with the goal of improving rural internet access across America. Yet just this week, the tech giant announced an expansion of the plan to connect over 40 million people to the internet by 2020, focusing on regions in Latin America and Sub-Saharan Africa. In the U.S., Microsoft has already introduced broadband access to 3 million Americans using unutilized TV White Space (TVWS) in the 600 MHz spectrum. Internationally, the company will use this TVWS strategy, alongside technologies derived from local partnerships, to overcome stifling government regulations and work with internet service providers (ISPs) along the way. Having already linked 6 million rural Columbians to the internet through partnerships with local ISPs, Microsoft has also helped deregulate TVWS in Ghana, enabling a broadband provider to offer its service to about 800,000 people.
Why it’s important: Today, almost half the world’s population is connected to the web, a percentage that continues to surge in response to satellite-provided connectivity, 5G, and drone networks. In rural areas isolated from technology hubs, internet access offers a path to countless new opportunities— educational, economic, social, imaginative. In one instance, by connecting two schools and five farms to the internet in Columbia (using TVWS), Microsoft has unlocked a plethora of free, digitized educational resources to local youth and adults alike. While this and similar initiatives (by tech giants like Facebook and Google) are partially incentivized by an expanded consumer base and financial gain, the rapid scaling of global connectivity also plays a critical social role in equalizing access to opportunities, regardless of one’s randomly assigned place of birth. | Share on Facebook.
Source
Want more conversations like this?
Abundance 360 is a curated global community of 360 entrepreneurs, executives, and investors committed to understanding and leveraging exponential technologies to transform their businesses. A 3-day mastermind at the start of each year gives members information, insights and implementation tools to learn what technologies are going from deceptive to disruptive and are converging to create new business opportunities. To learn more and apply, visit A360.com.
Abundance Digital, a Singularity University program, is an online educational portal and community of abundance-minded entrepreneurs. You’ll find weekly video updates from Peter, a curated news feed of exponential news, and a place to share your bold ideas. Click here to learn more and sign up.
Know someone who would benefit from getting Abundance Insider? Send them to this link to sign up.
(*Both Abundance 360 and Abundance Digital are Singularity University programs.)

